급성기 후기 자료
뇌졸중으로 인한 사망률을 줄이려면 급성기 이후 단계(치료 후 1~72시간)에는 다음과 같은 가장 일반적인 사망 원인 예방에 중점을 두어야 합니다 - 심장사(치명적 심근경색, 치명적 부정맥, 울혈성 심부전 포함), 폐렴, 재발성 뇌졸중, 패혈증 및 기타 원인.
급성기 후기 단계의 목표는 뇌졸중 후 조치의 품질과 일관성을 개선하고 뇌졸중 후 및 FeSS 체크리스트를 사용하여 모니터링하는 것입니다.
체크리스트
연하곤란 교육
뇌졸중/일과성허혈발작에서의 삼킴
Fever, Hyperglycemia, Swallow를 관리하는 간호사 주도 중재가 뇌졸중 발생 이후 사망과 일상 의존도를 현저하게 감소시키는 것으로 입증되었습니다. 다음 자료를 이용해 현재의 지식 수준을 높이고 평가해 보십시오.
삼킴장애 스크리닝 및 평가 프로토콜
뇌졸중 병동
뇌졸중으로 인한 사망률을 줄이려면 급성기 이후 단계(치료 후 1~72시간)에는 다음과 같은 가장 일반적인 사망 원인 예방에 중점을 두어야 합니다 - 심장사(치명적 MI, 치명적 부정맥, 울혈성 심부전 포함), 폐렴, 재발성 뇌졸중, 패혈증 및 기타 원인.
급성기 이후 단계의 목표는 뇌졸중 이후 및 FeSS 체크리스트를 사용하여 뇌졸중 후 진료의 품질과 일관성을 개선하고 모니터링하는 것입니다.
발열, 혈당, 삼킴 (FESS)
첫 72시간 동안 발열, 혈당, 삼킴(FeSS) 스크리닝 수행의 중요성과 FeSS 프로토콜을 적용하는 최선의 방법에 대해 배우십시오.
뇌졸중 팀 회의 의제
이 의제는 모든 병원에서 개최되어야 하는 주간 다학제 뇌졸중 팀 회의의 기초가 됩니다. 목표는 회의 시 병원에서 치료받고 있는 모든 환자를 간략히 소개하는 것입니다. 각 사례는 임상시험 계획서 이탈, 뇌졸중 치료 품질 매개변수, 환자 치료 계획의 관점에서 평가해야 한다. 이러한 단계를 지속적으로 따르면 치료를 표준화하고 지속적인 품질 개선이라는 사고방식을 고취할 수 있습니다. 이 회의에서 발생하는 \"해야 할 일\"은 이 안건의 조치 항목 섹션에 기록할 수 있습니다.
애로우 프로젝트
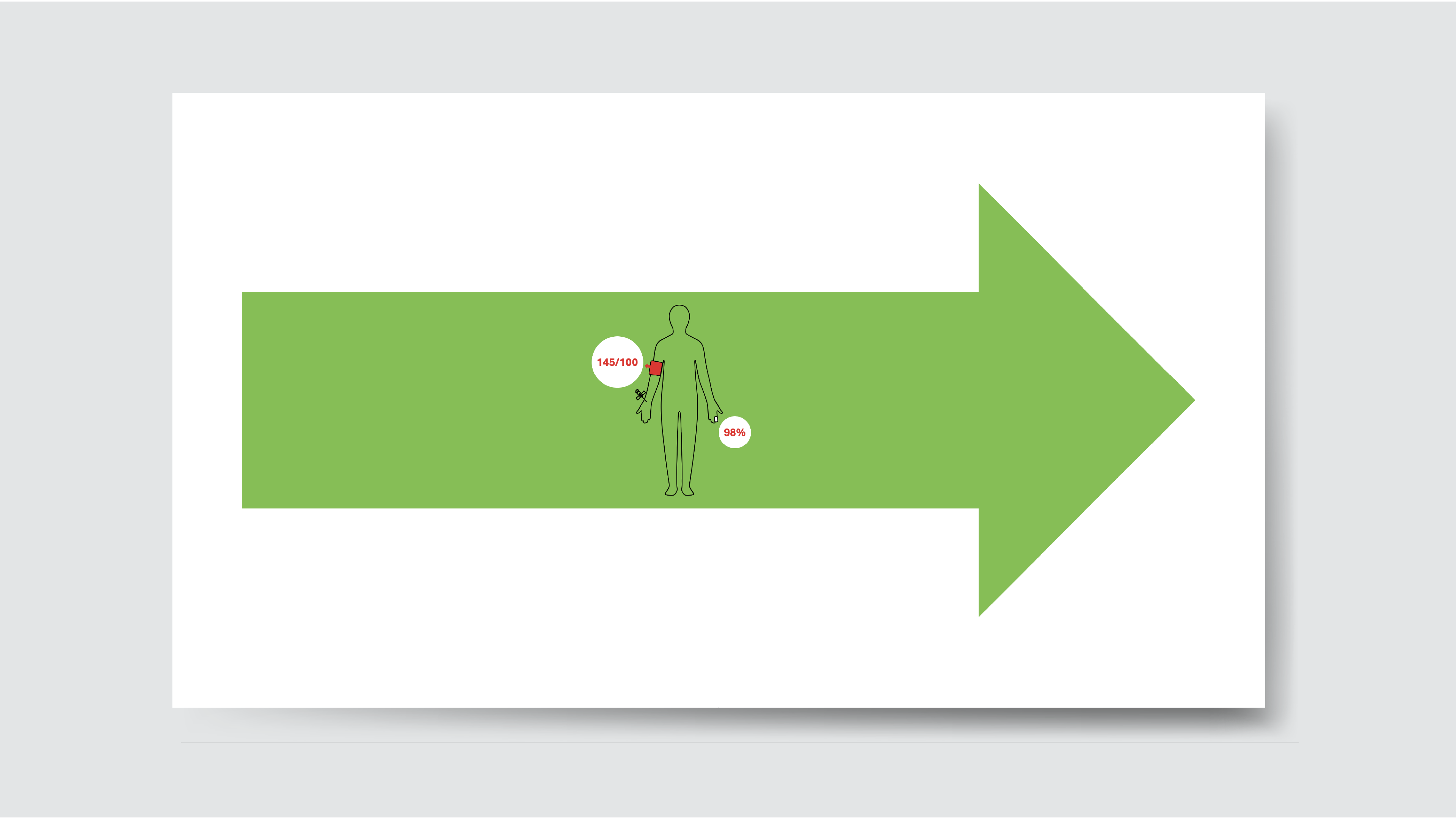
Arrow 프로젝트는 의사, 간호사, 심지어 포터가 뇌졸중 유형과 영향을 받는 측면을 쉽게 식별할 수 있도록 각 환자의 침대 위에 배치되는 색상 코드 화살표 시스템을 통해 급성 뇌졸중 후 치료를 표준화합니다. 매일의 치료 프로토콜에 대한 모든 세부 사항은 연하곤란, 혈당 및 발열에 대한 정기 점검과 같은 표를 통해 전달됩니다. 첫 번째 시각적 단서는 화살표 색상입니다. 즉, 출혈성 뇌졸중의 경우 빨간색, 허혈성 뇌졸중의 경우 노란색, 지주막하 출혈의 경우 녹색입니다. 두 번째 단서는 화살표의 방향입니다. 이는 영향을 받는 면을 나타내므로, 막 근무를 시작한 직원조차도 혈압 커프와 정맥 내 라인을 배치할 면, 혈중 산소 수치를 측정하기 위해 맥박 산소 측정기를 부착할 위치, 환자 동원에 접근하는 방법, 의사소통 능력이 손상된 환자에게 최적의 면이 무엇인지 즉시 알 수 있습니다.